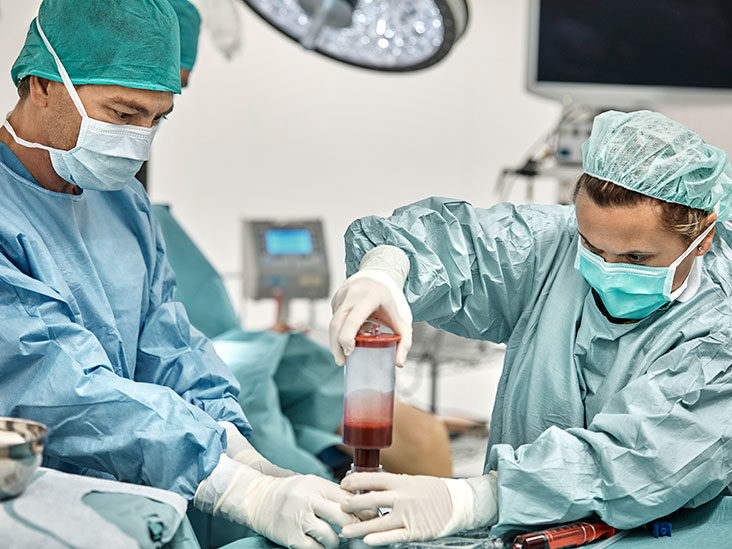
Patients with specific cancers or other disorders may benefit from bone marrow transplant (BMT), a specialized treatment. In a bone marrow transplant, stem cells which are often located in the bone marrow, are removed, filtered, and then given back to the donor or someone else.
After a person’s own unhealthy bone marrow has been treated to eliminate the abnormal cells, BMT aims to transfer healthy bone marrow cells into that individual. Here will a view of Bone marrow transplants for cancer treatment:
The procedure of Bone Marrow Transplant
The next operation will begin once the stem cells have been retrieved, which are necessary for the transplant. The next step is the necessary information for the process are:
- Most of the time, substantial radiation or chemotherapy dosages are used in the preparations. Intensive therapy is required for cancer to be effectively treated and to leave space in the bone marrow to develop new cells.
- This radiation or chemotherapy treatment is usually referred to as ablative or myeloablative due to its effect on the bone marrow. The bone marrow produces the majority of the blood cells in your body. When ablative therapy halts this cell-production process, the marrow becomes empty. The marrow must be empty for the new stem cells to grow and establish a new system for making blood cells.
- Following chemotherapy and radiation, the bone marrow transplant is given by a central venous catheter into the bloodstream. It is more like receiving a blood transfusion than undergoing surgery when the marrow is inserted into the bone. When the stem cells enter the bone marrow, they begin to divide and create new, healthy blood cells.
- After the transplant, supportive care is given to prevent and treat complications, adverse effects, and infections. Regular blood tests, careful vital sign monitoring, exact measurements of fluid intake and output, daily weigh-ins, and a clean and safe atmosphere are all part of it.
Types of Bone Marrow Transplant
Bone marrow transplants can be of two main types. The type will be chosen based on why you require a transplant.
i) Autologous Transplants
Autologous transplants involve the utilization of a patient’s stem cells. Typically, they involve taking a sample of your cells before initiating a cell-damaging therapy like chemotherapy or radiation. After the treatment, your body obtains its cells back. There are not always options for this type of transplant. It can only be applied if your bone marrow is in good condition. However, it reduces the chance of some severe side effects, such as GVHD.
ii) Allogeneic Transplants
Allogeneic transplants utilize donor cells as part of the healing process. The donor you choose should be your close genetic match. The best option is frequently a compatible relative, but genetic matches can also be located through a donor registry.
Allogeneic transplants are required if a disorder has damaged your bone marrow cells. However, they are more likely to experience some difficulties, like GVHD. In order to prevent your body from rejecting the new cells, your immune system will most likely need to be reduced with medicine. You may become more exposed to disease as a result. The similarity of the donor cells to your own determines whether an allogeneic transplant will be successful.
What is bone marrow transplantation used for?
Cancer cells are the objective of chemotherapy and radiation therapy, but healthy, quickly dividing cells can also be harmed. BMT is utilized to transplant healthy, cancer-free cells into the damaged bone marrow. Stem cell harm can happen as a result of:
- Cancer treatment
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation treatment
BMT is unsuccessful as a preventative measure. Additionally, damage cannot be rectified if the bone marrow is gone. Damage to the bone marrow can result from:
- Bone marrow-directed chemotherapy and radiation therapy are frequently used to treat blood cancers such as leukemia and lymphomas.
- Systemic therapy has an impact on all bodily cells, including stem cells.
The following cancers are most typically treated with BMT and PBSCT:
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
- Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
- Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
- Multiple myeloma
- Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- Neuroblastoma
How long does a bone marrow transplant take to recover from?
- For the first several weeks and months after being discharged from the hospital, the patient will need to visit an outpatient clinic often. This will make it possible for medical personnel to monitor the patient’s progress. With time, these excursions will occur less frequently.
- The clinic’s medical staff will offer the patient and their caregiver instructions on how to look for and prevent infections, maintain their central line, and perform other medical procedures.
- Following a bone marrow transplant, recovery time may be prolonged. Restoring average blood cell counts and immunological function takes six to twelve months. Take care to prevent infections, get enough rest, and follow your doctor’s prescriptions for medications and checks throughout this period.
Benefits of Bone Marrow Transplant
Lower risk of diseases linked to obesity
Adiponectin is a hormone shown in studies to be present in bone marrow fat tissue. This hormone helps with fatty food digestion. Its capacity to maintain insulin sensitivity has been associated with a decreased incidence of diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other cancers related to obesity. A higher amount of adiponectin is linked to a reduced risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Adiponectin levels were lower in overweight adults, but as they lost weight, they increased.
Maintain healthy skin, bones, and joints
The abundance of collagen in bone marrow improves the health of the muscles, skin, and bones. Additionally, it contains glucosamine, a substance that reduces joint inflammation, eases joint discomfort, and helps to prevent osteoarthritis.
Lowers risk of illnesses linked to inflammation
The bone marrow contains large amounts of glycine, which has been discovered to have potent anti-inflammatory effects, and conjugated linoleic acid. Chronic inflammation is linked to a number of diseases, including cancer, heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, depression, and Alzheimer’s.
Bone Marrow Transplant in India
India is one of the most advanced medical tourism destination for cancer patients from all over the world. Top Indian hospitals offers bone marrow transplant treatment for cancer patient at affordable cost.
The bone marrow transplant cost in India is not only affordable but also the quality of treatment matches the standard of any top hospital in the world, therefore bmt transplant surgery in India can be a perfect for cancer patient who is looking for affordable treatment.
Bottom Line
A highly skilled physician must be consulted if you are considering a bone marrow transplant. They will evaluate your physical condition before beginning the treatment process. These are the conditions and illnesses that bone marrow transplants can treat.
Make Money Online