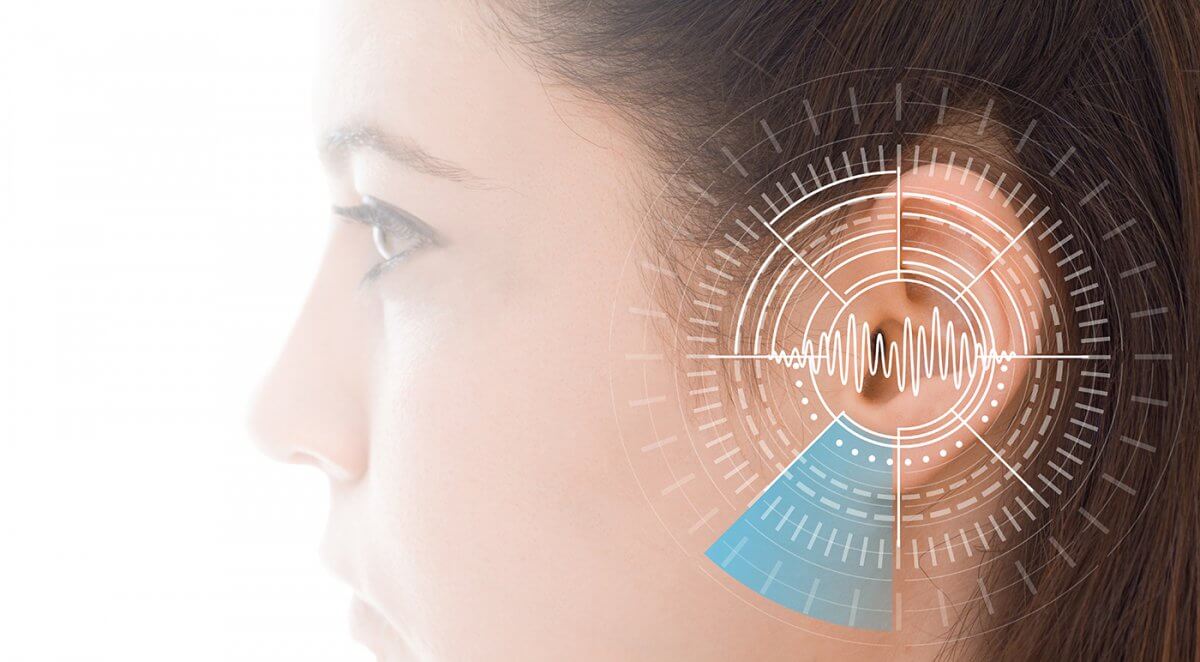
symptoms of hearing loss
For grown-ups with any kind of hearingl loss, these are each good pointers that you may not be hearing as well as you used to. After witnessing all these things. Visit an audiologist or Hearing aid in Hyderabad.
- musketeers or family say you turn the TV or radio over too loud
- You struggle to understand speech, especially in noisy surroundings
- Phone conversations are difficult for you
- Hearing, but not understanding, a feeling
- You aren’t sure where sound is coming from, known as localization
- You frequently ask people to repeat themselves
- You are dependent on a partner or a loved one to help you hear
- You find yourself avoiding social situations
- You feel prostration after attending social events, known as harkening fatigue
- You notice tinnitus, or ringing in the cognizance
- Paradoxically, some sounds feel too loud, known as” reclamation”
Symptoms by Hearing loss type
- Sounds with high frequencies and high pitches are difficult to hear
- A notch in the noise level makes it difficult to hear some high-pitched sounds
- Mid-rangemid-range sounds are hard to hear
- Having a hard time hearing low-frequency sounds
- Conductive( general) Hearing loss from damage to middle or external observance
- Unforeseen Hearing loss onset is rapid-fire
- There is a difficult time hearing all pitches when the pitch is flat
- Single- sided only one observance is affected
- Temporary noise related the Hearing loss may go down
Hearing loss from inner observance or whim-whams damage( sensorineural)
The most common type of Hearing loss is sensorineural Hearing loss, which is caused from damage to the delicate hair cells in the inner observance and/ or the whim-whams pathways that deliver sound to your brain. About 90 of people with Hearing loss have this type, and it has a wide range of causes.
Volume and clarity are affected
Sensorineural Hearing loss is generally gradational you do not wake up overnight not being suitable to hear. rather, you sluggishly lose the capability to hear. Both how loudly( volume) and how easily( clarity) you perceive sound are affected. You might also witness a miracle known as reclamation, which causes some louder sounds to be uncomfortable to hear to. For illustration, you formerly loved fireworks shows, but now find the booming sounds nearly unsupportable.
Sensorineural Hearing loss can affect all ranges of Hearing, including the exemplifications below. Low-pitched sounds may be hard for some people to hear, while high-pitched sounds may not be hard for others. One observance may hear better than the other, too. There is wide variability among people, indeed with the same type of Hearing loss. Have you had a Hearing test, but do not understand the results? This manual on how to read an audiogram can help.
High- frequence Hearing loss symptoms
One of the more common types of sensorineural Hearing loss is high- frequence Hearing loss, which appears as a” ski pitch” pattern on an audiogram. numerous people who have presbycusis, a type of age-affiliated Hearing loss, develop this kind of Hearing loss. It results in the reduced capability to hear effects like
Symptoms of noise- notch Hearing loss
analogous to high- frequence Hearing loss, noise- notch Hearing loss means you can not hear certain high-pitched sounds veritably well( similar as children’s voices). But unlike high- frequence Hearing loss, you may still hear veritably high-pitched sounds( catcalls or beeps). This type of Hearing loss is associated with noise- convinced Hearing loss, especially loud gun blasts. For illustration, nimrods who develop shooter’s observance frequently have a noise- notch pattern of Hearing loss.
Symptoms of’ cookie- bite’ Hearing loss(mid-range frequence loss)
Less common than high- frequence Hearing loss,” cookie- bite” Hearing loss( which gets its name from its distinctive pattern on an audiogram) is when a child or grown-up has trouble hearing sounds in themid-range frequentness. There is no particular pitch to these sounds. As you can imagine, this includes numerous common sounds, making everyday situations like talking to musketeers or harkening to music grueling . Generally people with this kind of Hearing loss will realize they can fluently hear effects like squealing admonitions or roaring thuds, yet struggle to hear speech or music at what are putatively normal volumes for other people.
Symptoms of low- frequence loss( rear- pitch)
Rarer still, rear- pitch Hearing loss is basically the contrary of high- frequence Hearing loss. Symptoms include chancing men’s voices harder to hear than women’s or children’s voices, floundering to hear people on the phone but not so much during face- to- face exchanges, and incapability to hear environmental sounds that are low-pitched, similar as the bass in music or thunder. A person with rear pitch Hearing loss also might feel surprisingly sensitive to high-pitched sounds, too. occasionally, Meniere’s complaint can beget this type of Hearing loss in the earlier stages of the complaint.
Conductive Hearing loss symptoms
About 10 of people with Hearing loss have conductive Hearing loss, which means that their inner observance works OK , but their external or middle observance is not working typically for some reason( causes can range from a severe earwax blockage to head trauma). utmost other types of endless conductive Hearing loss are detected at birth or soon after.
In grown-ups, when it does do, it tends to develop must briskly than sensorineural Hearing loss, and depending on the cause, may be reversible. The symptoms will be analogous to general Hearing loss symptoms, just being at a faster rate. For illustration, if you’re in a bad auto accident and notice you are floundering to hear speech, and feel like your own voice sounds odd to you, you may have conductive Hearing loss. Any pain, pressure, or strange odor in your cognizance are other suggestions you may have a condition that causes conductive Hearing loss.
Symptoms of unforeseen Hearing loss
In rare cases, a person can develop unforeseen Hearing loss, generally in one observance. It may be conductive or sensorineural. The symptoms and signs are generally enough egregious you suddenly can not hear well out of one observance. But if you have a bad cold wave or observance infection, it may be hard to tell if it’s just temporary traffic or factual Hearing damage from the contagion or bacteria. In some cases, people hear a loud pop and also lose their Hearing. The affected observance may feel stuffy, or” full,” and a person may feel dizziness or Hearing ringing in your observance. Because prompt treatment is crucial, act presto if you witness unforeseen Hearing loss.
Flat Hearing loss symptoms
Some causes of conductive unforeseen Hearing loss can lead to what is known as” flat” Hearing loss. This is when you struggle to hear sounds across the noise diapason downward – pitched, normal and high- pitched. All sounds would be harder to hear compared to a person with normal Hearing.
Symptoms of single- sided deafness
For people with severe to profound Hearing loss in one observance, you may notice it’s harder to tell where sound is coming from, known as localization. You also may have a hard time fastening on a single source of sound in a noisy terrain, similar as at a party. You might also struggle to discern how loud a sound is, because your brain relies on sensitive input from both cognizance to descry volume. People with single- sided nothingness also witness commodity known as as the” head shadow” effect, which makes high-pitched sounds harder to hear.
Temporary noise-affiliated Hearing loss symptoms
Temporary Hearing loss is frequently related to exposure to loud noises, similar as gunfire, fireworks, musicales or exposure at work. Temporary Hearing loss is characterized by a temporary threshold shift( TTS), meaning that you temporarily will not hear as well. It’s frequently accompanied by tinnitus, or ringing in the cognizance. It can last for only a many hours or several days before hearing returns to normal.
The cognizance have a harder time recovering from TTS after each circumstance. Any regular noise exposure puts you at threat of Hearing loss, including noise- notch Hearing loss( see over), linked to noise- convinced Hearing loss. You can avoid this by learning how to help Hearing loss.
Symptoms of Hearing loss in children
Hearing loss in children is generally detected with the help of a invigorated child Hearing webbing soon after birth. Some parents also may be suitable to descry Hearing loss in their child if it’s not caught at birth.
Symptoms of Hearing loss in children include
- A detention in speech and language development
- Child doesn’t startle when loud sound is present
- Child can not localize sound( tell where sound is coming from)
- Poor performance in academy
- Behavioral problems in academy
- A literacy disability opinion
Signs of Hearing loss
A” sign” is what a health care provider can descry with testing or a medical test( and a” symptom” is what you notice but can not inescapably be measured). To look for the signs of Hearing loss, a Hearing care provider will generally start with questions about symptoms you are passing, and also conduct a formal Hearing test to see how well you hear beep- suchlike sounds( known as a pure- tone test), speech in noise and other sounds. Your Hearing is also colluded on an audiogram that shows the extent of your Hearing loss in both cognizance. Then is how to know if you need your Hearing tested.